Basic Physics for Wireless Communications - Electromagnetic Wave
With the development of science and technology, radio wave applications have penetrated into every aspect of our lives!
Radio/TV; mobile phone communication, Wi-fi Bluetooth, infrared remote sensing.
To understand wireless transmission, first we need to understand the basic physical knowledge: electromagnetic waves.
What are Electromagnetic Waves?
A fluctuation of a small group of energy with 2 related physical properties, wavelength and frequency; the relationship between the two is observed Wavelength x Frequency = Speed of Light.
Radio waves used for Radio, TV , mobile phone communication , Wi-fi and Bluetooth are a kinds of electromagnetic waves between the sound waves that we can hear and the light that is visible to the human eyes, the frequency from 300KHZ – 300GHZ ,Wavelength about from 1mm-1km, collectively known as RF (Radio Frequency).Transmit and receive via antenna.
Applications of different frequencies in life from 1HZ to 1024 HZ
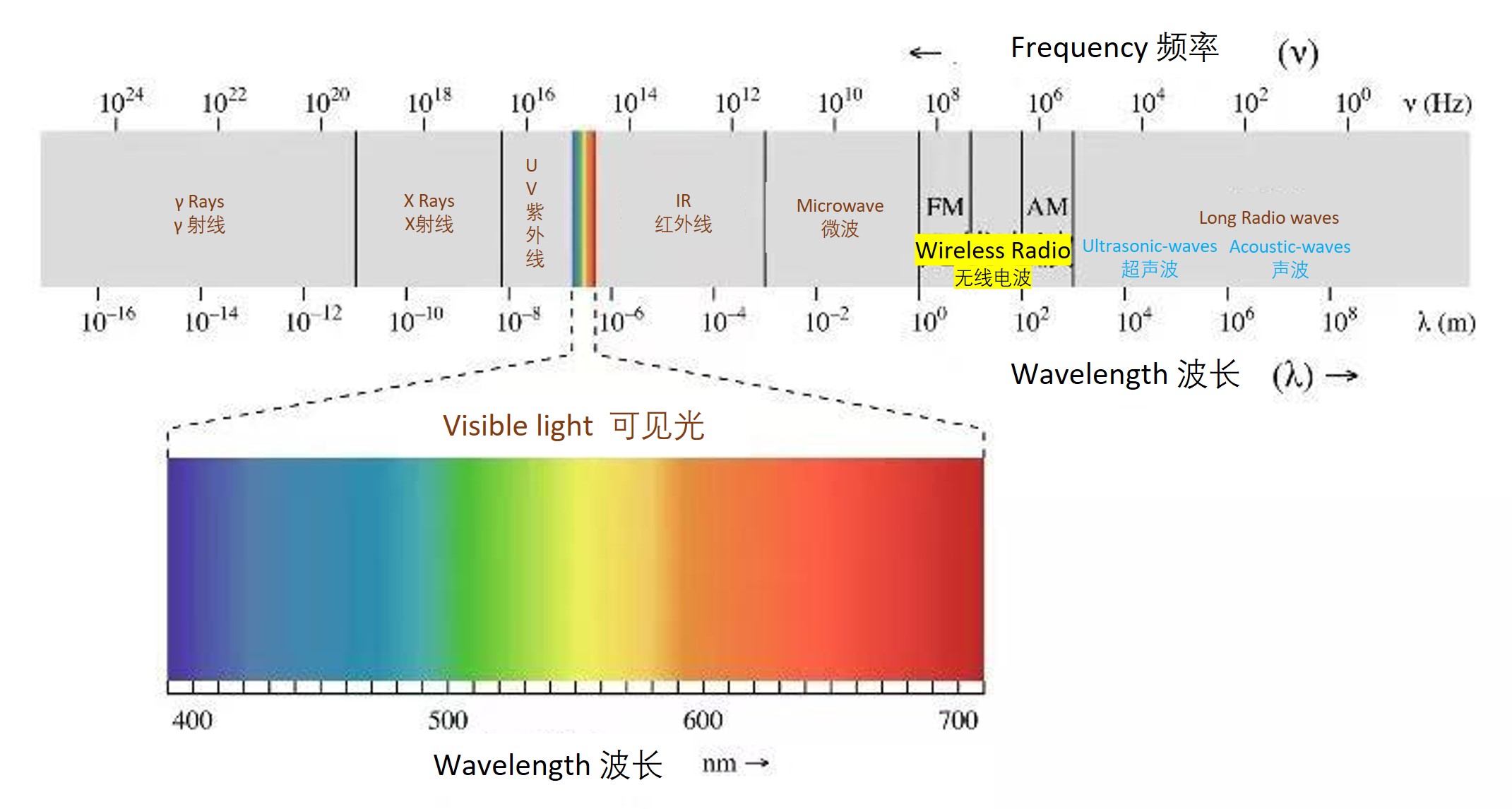
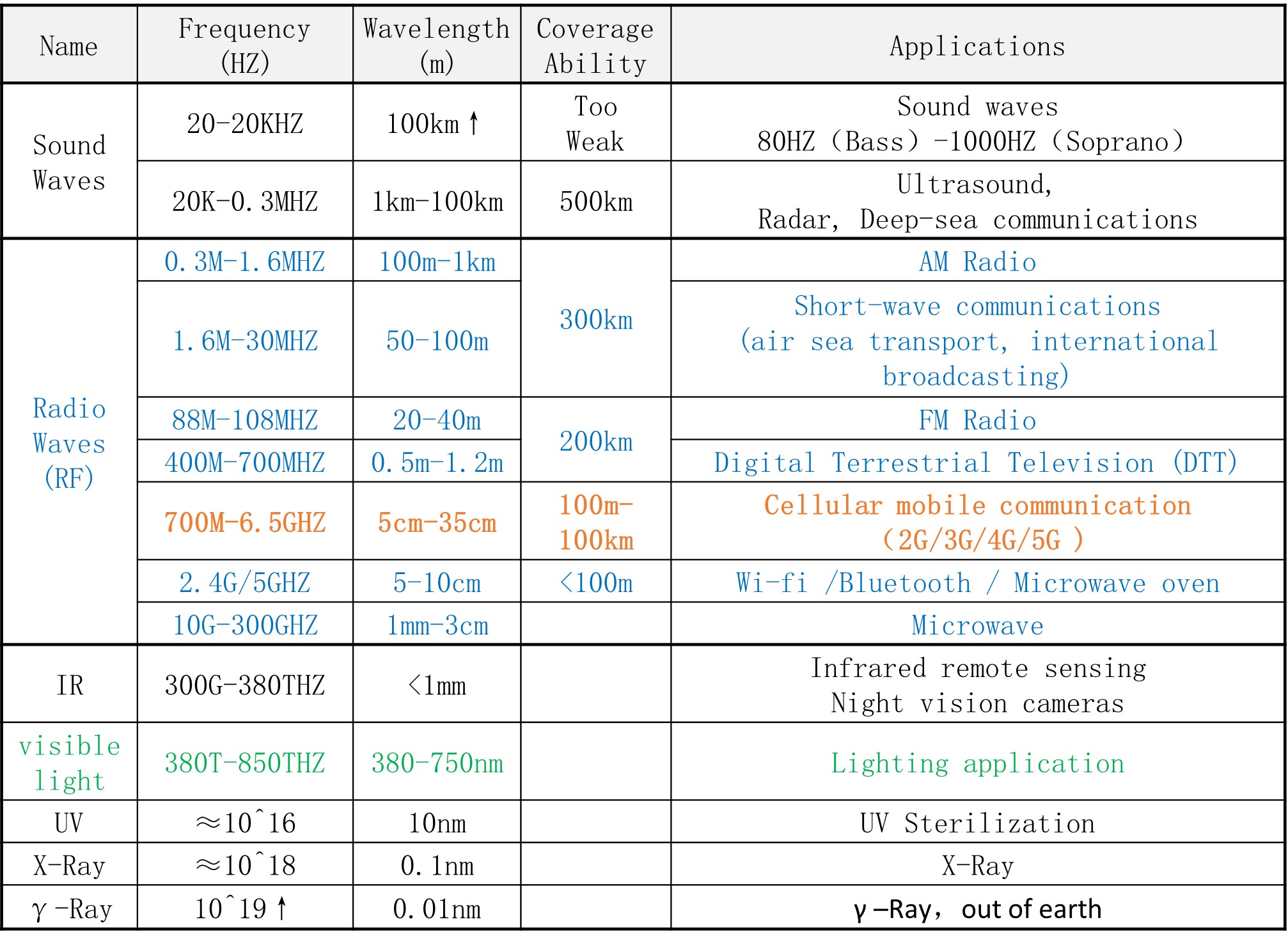
From the above table, we can see that as the frequency increases, the shorter the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave, the weaker the penetration, the transmission distance and the ability of coverage also decreases, but the damage to the human body will be enhanced!
Here, we dismantle a pseudo-science, many of us in the use of electronic devices will worry about electromagnetic radiation damage to health, is this true? There are times when we can threaten our children in this way so they don't get addicted to video games, but the truth is:
Usually only higher than the visible light frequency radiation on the body has a health impact, RF is much lower than the frequency of infrared light electromagnetic waves, the use of mobile phones when the radiation is much weaker than the energy of the light irradiation at night, during the day we are able to embrace the sunshine, so there is no need to really worry about communication antenna mounted on the roof of the impact on health!

